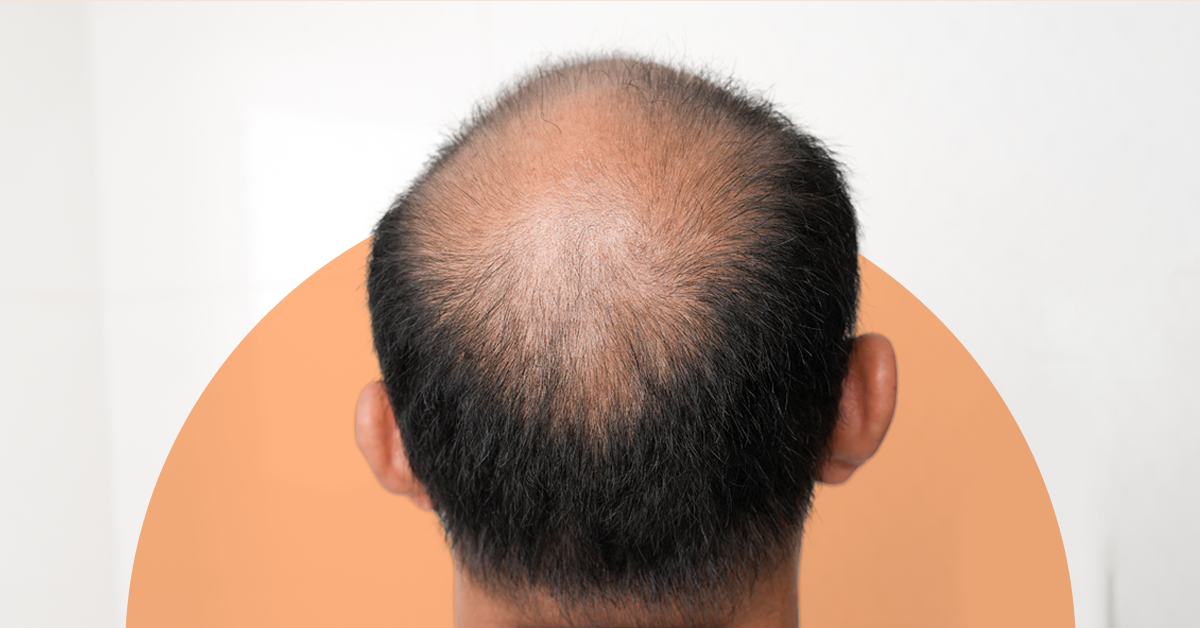
Alopecia areata is a medical condition where one’s immunity attacks the hair follicles, causing hair loss in patches. Follicles are the structures on our scalp that aid in the formation of hair on our bodies. This condition can occur in any part of the body, but it is more common in the face and head. Healthy individuals developing this disorder usually show no symptoms, and it’s not completely curable. Nevertheless, few treatment methods can help one’s hair grow back. Here is an overview of alopecia areata and its symptoms, causes, and treatment.
Overview: What is Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disorder resulting in hair loss on the scalp, face, and other body areas. It occurs when our immune system attacks the hair follicles causing hair loss. The condition can affect people of all ages and genders, but it is mostly diagnosed in children and young adults.
Who Can Get Alopecia Areata?
Research has shown that it tends to occur more frequently in individuals with a family history of the condition or other autoimmune disorders. It also tends to affect younger people more often, with the onset typically occurring before the age of 30. Additionally, factors such as high-stress levels, certain medications, and viral infections have been linked to the development of alopecia areata.
Signs and Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
The alopecia areata symptoms can vary from person to person, but the most common symptoms are:
Patchy hair loss:
Alopecia areata often causes round or oval patches of hair loss on your scalp or other parts of the body.
Rapid hair loss:
The hair loss associated with alopecia areata can occur suddenly and rapidly over a few days or weeks.
Bald spots:
As the condition progresses, the bald spots may become larger, creating more widespread hair loss.
Itching or burning:
Some people may experience itching, burning, or tenderness in the affected areas before hair loss occurs.
Nail changes:
In some cases, alopecia areata can affect the nails, such as pitting, ridges, or a thinning of the nails.
Causes of Alopecia Areata
The exact alopecia areata causes are not yet fully understood, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental causes of alopecia may be involved.
Autoimmune disorder:
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks our hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Genetics:
A family history of alopecia areata can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
Environmental triggers:
Some environmental factors, such as viral infections, emotional stress, and physical trauma, may trigger the onset of alopecia areata in individuals genetically susceptible to the condition.
Hormonal changes:
Hormonal changes occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, may also play a role in the development of alopecia areata.
Medications:
Certain medications, such as those used to treat cancer or autoimmune disorders, may cause hair loss as a side effect and can sometimes trigger alopecia areata.
Alopecia areata treatment options
Although there is presently no alopecia cure, doctors might recommend several kinds of alopecia areata treatment to hasten the growth of new hair.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that can be applied topically, injected into the affected area, or taken orally. They can help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, which can help promote hair regrowth.
Topical Immunotherapy
This medicine for alopecia involves applying a chemical irritant to the affected area, which stimulates the immune response and promotes hair regrowth.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is a popular topical medication commonly used for treating hair loss. This alopecia areata cure can help stimulate hair growth and improve hair quality.
Anthralin
Anthralin is a topical medication commonly used to treat psoriasis, but it can also effectively promote hair regrowth in alopecia areata. It works by suppressing the immune system and stimulating hair growth.
Hair Transplant Surgery
In a few cases, hair transplant surgery may be an option for individuals with alopecia areata with extensive or permanent hair loss. During this alopecia treatment for men and women, hair follicles get transplanted from one area of the scalp to the affected area. This can help improve the appearance of the scalp and promote hair regrowth.
Conclusion
A thorough examination and medical history of the hair and scalp are typically sufficient to determine the reason for your hair loss. Discover the root of the problem and begin treatment as soon as you discover you’re losing more hair than usual. Even though over-the-counter alopecia areata medications may stop hair loss, contacting a doctor is important because other health issues might also result in hair loss.
FAQs related to alopecia areata
Does alopecia areata go away?
This condition is not curable, but various alopecia treatment methods can help hair grow back.
Is alopecia areata serious?
Despite the disease’s lack of major medical effects, it can psychologically affect individuals.
Can your hair grow back if you have alopecia areata?
Most patients ultimately have new hair growth in the affected regions, but it may take months.
How do you know if you have alopecia areata?
The symptoms of alopecia are sudden hair loss in patches that can grow larger.
What are the beginning stages of alopecia?
The early signs of alopecia include round, small patches of hair loss on the beard, scalp, and other hairy regions of the body.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information contained herein is not a substitute for and should never be relied upon for professional medical advice. Book a consultation with andSons medical team to learn more about healthcare treatments here.