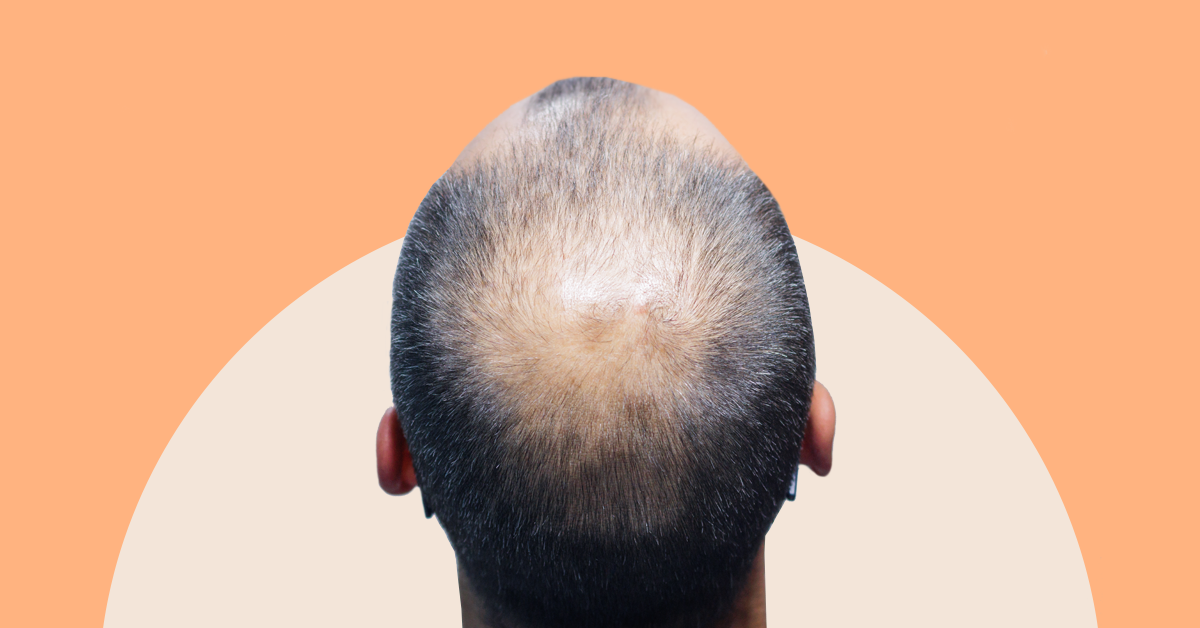
The growing prevalence of androgenic alopecia among men makes it an important topic to understand. While the cause of this condition remains unknown, it is believed to be related to genetics or hormones. Thankfully, there are many androgenic alopecia treatments available to address this issue.
This article will discuss the stages, causes, and treatment options for Androgenic Alopecia men. With so many solutions available, there’s no need to suffer from hair loss any longer!
Let’s get started.
An overview of androgenic alopecia
Androgenic alopecia known as male pattern baldness, is men’s most common type of hair loss. It’s characterised by a receding hairline and thinning on the crown and can start as early as adolescence. It affects up to 70% of men in their lifetime and can significantly impact self-esteem. Fortunately, a new treatment for androgenic alopecia is available that may help slow down or reverse Androgenic Alopecia.
Stages of androgenic alopecia
Stage 1:
In this stage, there is minimal hair loss, and the scalp appears to have a normal density of hair.
Stage 2:
There is a slight hairline recession in this stage, usually in the temporal region. Hair loss may also occur in the crown area of the scalp.
Stage 3:
Significant hair loss in the temporal region creates an “M” shape hairline. Hair loss may also be more apparent in the crown area.
Stage 4:
In this stage, further hair loss in the crown area creates a bald spot. The hairline continues to recede, and the hair on the sides of the head may also begin to thin.
Stage 5:
In this stage, the bald spot in the crown area becomes larger, and the hairline continues to recede further. The hair on the sides of the head may also be noticeably thinner.
Stage 6:
In this stage, the hair loss in the crown area and the hairline is more extensive, leaving only a hair strip at the head’s sides and back.
Stage 7:
In this final stage, only a narrow band of hair remains on the sides and back of the head. Hair loss is severe, and the scalp is visible.
Symptoms of male pattern baldness
The androgenic alopecia symptoms are as follows:
Miniaturisation of hair:
As androgenic alopecia progresses, the hair follicles may become smaller and produce thinner and shorter hair.
Itching or burning sensation:
Some individuals with androgenic alopecia may experience an itchy or burning sensation on their scalp.
Hair loss on other parts of the body:
Androgenic alopecia can cause of hair loss on other body parts, including the beard or eyebrows.
Psychological impact:
Androgenic alopecia can have a significant psychological impact on individuals, causing low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression.
Causes of androgenic alopecia
The androgenic alopecia causes are as follows:
Genetic factors:
Androgenic alopecia is primarily caused by genetic factors, with a family history of the condition being a significant risk factor.
Hormonal imbalances:
The primary hormone responsible for androgenic alopecia is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a testosterone derivative.
Age:
Androgenic alopecia is more common as individuals age, affecting approximately 50% of men by age 50.
Medical conditions:
Certain medical conditions including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders, can result in hormonal imbalances contributing to androgenic alopecia.
Medications:
Certain medications, such as anabolic steroids and some blood pressure medications, can cause androgenic alopecia as a side effect.
Treatment for androgenic alopecia
Minoxidil:
This topical medication can help slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth.
Finasteride:
You need to take this medication by mouth, and it works by preventing the conversion of testosterone into DHT.
Hair transplant surgery:
This process entails moving hair follicles from regions of the scalp with robust hair growth to areas that have hair loss or reduced density.
Low-level laser therapy:
This treatment uses special light therapy to stimulate hair growth.
Conclusion
Androgenic alopecia is a form of hair loss that affects many men and can be devastating for those affected. You must consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the multiple stages, causes, and treatments available for this condition to determine the most appropriate course of action. With proper treatment options available, it is possible to slow or even stop the progress of androgenic alopecia.
FAQs
Can androgenic alopecia be stopped?
Yes, it is possible to stop the progression of androgenic alopecia, but treatment must be started early and consistently.
Can androgenic alopecia regrow hair?
Yes, it is possible to regrow hair lost due to androgenic alopecia. However, the extent of regrowth depends on the individual’s response to treatment. The most common treatments for androgenic alopecia are topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
How does male pattern baldness affect?
Male pattern baldness usually affects men but can also affect women. It is caused by the hormone dihydrotestosterone which results in hair follicles shrinking and stop producing hair.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information contained herein is not a substitute for and should never be relied upon for professional medical advice. Book a consultation with andSons medical team to learn more about healthcare treatments here.